The energy we use to power our homes, businesses and lives plays a crucial role in shaping our environment. Today, there is a growing awareness of the impact of our energy choices on the environment. While the energy industry is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels, there is a shift towards renewable energy sources like solar power.
In this blog post, we will dive into the environmental sustainability divide between solar power and fossil fuels. From examining the benefits and drawbacks of each energy source to understanding the environmental impact of their use, we will explore which option is more sustainable for our planet. Join us as we unveil the truth about these two important energy sources, and how they affect our planet.
Introduction: The pressing need for sustainable energy sources
In today’s rapidly changing world, the need for sustainable energy sources has never been more pressing. As the global population continues to grow, so does the demand for energy to power our homes, businesses, and industries. However, our current reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is not only depleting our finite resources but also causing irreparable damage to our environment.
The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to the acceleration of climate change. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and the melting of polar ice caps are just some of the devastating consequences we are already witnessing. It is clear that we must transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy alternatives to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Solar power emerges as a beacon of hope amidst this environmental crisis. Harnessing the energy of the sun, solar power offers a renewable and virtually unlimited energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power does not produce harmful emissions during operation, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution. By embracing solar energy, we can reduce our carbon footprint and work towards a greener future.
In this blog post, we will delve into the comparison between solar power and fossil fuels, exploring the environmental sustainability divide. We will examine the benefits and drawbacks of each energy source, considering factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, resource availability, and long-term viability.
By shedding light on this important topic, we aim to empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions about their energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable world. Let’s embark on this journey together, uncovering the potential of solar power in transforming our energy landscape and preserving our planet for future generations.
Understanding the environmental impact of fossil fuels
Fossil fuels have long been the dominant source of energy worldwide, powering industries, transportation, and homes. However, it is crucial to understand the environmental impact associated with their usage. The extraction, refining, and burning of fossil fuels release significant amounts of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, contributing to the phenomenon known as global warming and climate change.
Not only do fossil fuels contribute to climate change, but they also have detrimental effects on local ecosystems. The extraction processes, such as mining and drilling, often lead to habitat destruction and soil erosion. Additionally, accidents during extraction or transportation can result in devastating oil spills or gas leaks, causing severe damage to marine and terrestrial environments.
The reliance on fossil fuels also poses health risks to both humans and wildlife. The combustion of these fuels releases pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which can contribute to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even premature death. These pollutants can also harm ecosystems, leading to the decline of sensitive species and the degradation of air and water quality.
Furthermore, the extraction and transportation of fossil fuels are energy-intensive processes that require significant amounts of water and can deplete valuable natural resources. This depletion can have negative consequences on local communities and ecosystems, affecting access to clean water and disrupting delicate ecosystems.
Understanding the environmental impact of fossil fuels is crucial in assessing their sustainability and exploring alternative energy sources. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, embracing renewable energy, such as solar power, becomes increasingly important. Solar power offers a cleaner and more sustainable alternative, harnessing the energy of the sun without releasing harmful pollutants or contributing to climate change.
By comprehending the environmental consequences of fossil fuels, we can make informed decisions and work towards a more sustainable future powered by renewable energy sources like solar power, reducing our carbon footprint and preserving the planet for generations to come.
The advantages of solar power for the environment
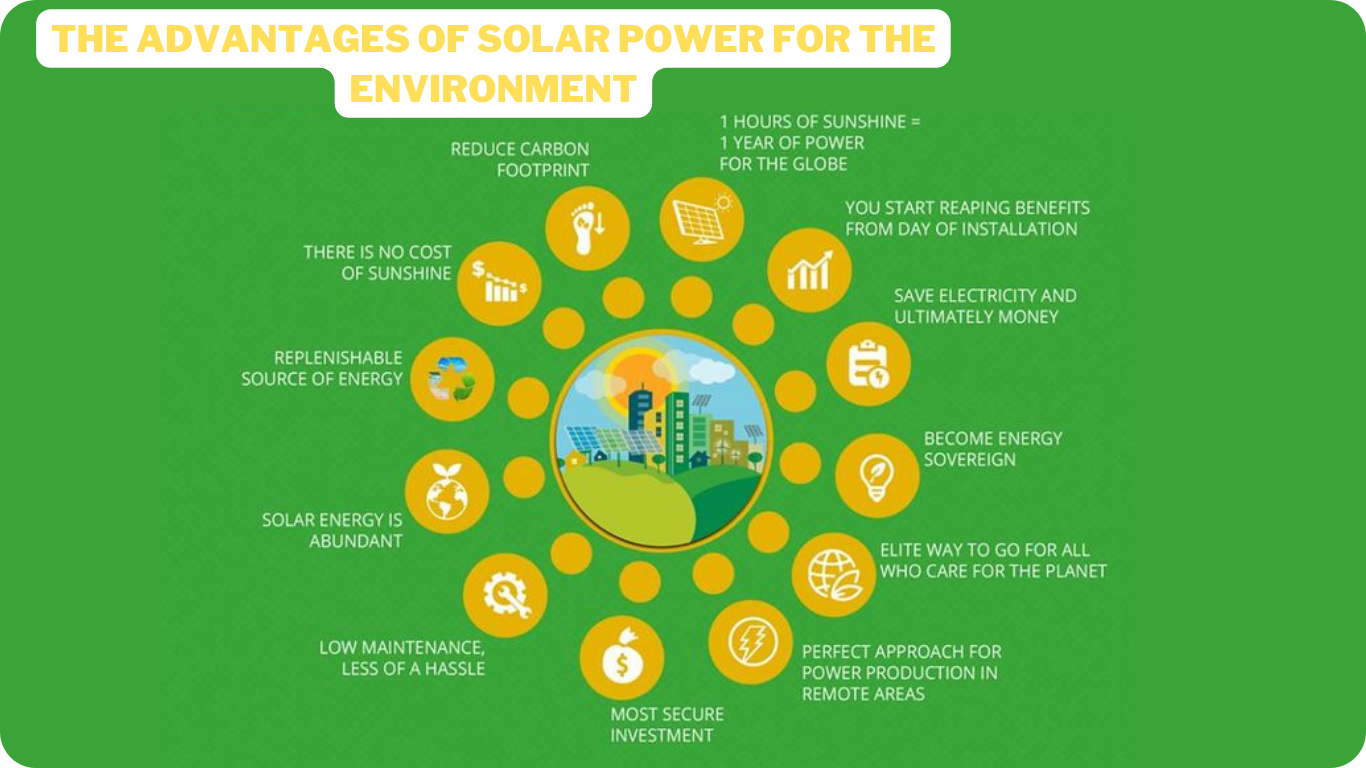
Solar power offers numerous advantages for the environment, making it a sustainable and clean energy source. One of the primary benefits is its significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants when burned, solar power generates electricity without emitting any greenhouse gases. This plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and reducing the overall carbon footprint.
Another advantage of solar power is its ability to conserve water resources. Traditional power plants that rely on fossil fuels consume vast amounts of water for cooling and other operational purposes. In contrast, solar energy systems require minimal water for maintenance, resulting in significant water savings. This is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity or drought conditions, where every drop counts.
Furthermore, solar power helps to decrease reliance on finite fossil fuel resources. Fossil fuels are non-renewable and will eventually run out, leading to potential energy crises and global instability. Solar energy, on the other hand, is abundant and available throughout the world. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and move towards a sustainable energy future.
In addition to these environmental benefits, solar power also enhances air quality. Traditional energy sources like coal and oil contribute to air pollution, releasing pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants have detrimental effects on human health, leading to respiratory problems and other illnesses. Solar power eliminates these emissions, improving air quality and creating healthier living environments for communities.
Overall, the advantages of solar power for the environment are clear. It offers a clean, renewable energy source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions, conserves water resources, decreases reliance on finite fossil fuels, and improves air quality. Embracing solar power not only helps combat climate change but also promotes a healthier, more sustainable planet for future generations.
Read it also : Innovations Driving the Solar Power Revolution: Shining a Light on the Future 2023
Comparing greenhouse gas emissions: Fossil Fuels vs. Solar Power
When it comes to comparing greenhouse gas emissions, the divide between solar power and fossil fuels becomes increasingly apparent. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have long been the primary sources of energy production. However, their extraction, processing, and combustion release significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
On the other hand, solar power offers a cleaner and more sustainable alternative. Solar energy systems harness the power of the sun to generate electricity, without emitting any greenhouse gases during the generation process. The photovoltaic (PV) cells in solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, making it a renewable and emission-free energy source.
Research has shown that solar power produces negligible greenhouse gas emissions throughout its entire lifecycle, from manufacturing to operation. In contrast, fossil fuel-based power plants emit substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and other harmful pollutants when extracting, transporting, and burning these non-renewable resources.
Furthermore, the extraction of fossil fuels often involves destructive practices like mountaintop removal mining or deep-sea drilling, which have detrimental impacts on ecosystems and biodiversity. Solar power, on the other hand, has a minimal ecological footprint and can be integrated into existing structures or installed in solar farms without significant environmental disruption.
It is worth noting that while solar power itself has minimal greenhouse gas emissions, the production and disposal of solar panels do have some environmental impact. However, advancements in technology and manufacturing processes continue to reduce these impacts, making solar power an increasingly sustainable choice.
In conclusion, when comparing greenhouse gas emissions, solar power stands out as a clear winner in terms of environmental sustainability. By embracing solar energy and transitioning away from fossil fuels, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint, mitigate climate change, and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
The impact on air and water quality: Fossil Fuels vs. Solar Power
When comparing solar power and fossil fuels, one of the key factors to consider is their impact on air and water quality. Fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, have long been notorious for their detrimental effects on the environment. The combustion of these fuels releases harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and the formation of greenhouse gases.
On the other hand, solar power is a clean and renewable energy source that emits virtually no air pollutants during its operation. Solar panels harness the energy from the sun and convert it into electricity without the need for burning fossil fuels. This means that solar power does not release harmful emissions like carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen oxides, which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change.
Additionally, the extraction and transportation of fossil fuels can have significant impacts on water quality. Oil spills and leaks from pipelines or offshore drilling operations can lead to devastating consequences for marine ecosystems and water sources. The process of hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, used to extract natural gas from underground shale formations, can also contaminate water supplies with chemicals and pollutants.
In stark contrast, solar power systems have minimal impact on water resources. While some water may be used during the manufacturing and maintenance of solar panels, it is significantly less compared to the vast amounts required for fossil fuel extraction and cooling in power plants.
By choosing solar power over fossil fuels, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the negative effects on air and water quality. Embracing solar energy is a crucial step towards creating a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly future.
Land use and habitat destruction: Fossil Fuels vs. Solar Power
When it comes to land use and habitat destruction, there is a clear distinction between solar power and fossil fuels. Fossil fuel extraction and mining operations often require large areas of land to be cleared, leading to deforestation and destruction of natural habitats. This not only disrupts ecosystems and displaces wildlife but also contributes to soil erosion and degradation.
On the other hand, solar power systems typically require much less land and can be integrated into existing infrastructure such as rooftops or unused land. Solar panels can be installed on buildings, parking lots, or even floating on bodies of water, minimizing the need for additional land use. This allows for the preservation of natural habitats and reduces the impact on biodiversity.
Furthermore, the extraction and transportation of fossil fuels can have devastating consequences for fragile ecosystems, such as oil spills in oceans or the destruction of forests during the construction of pipelines. These incidents can lead to long-term environmental damage and have detrimental effects on wildlife and marine life.
Solar power, on the other hand, does not involve such risks. Once installed, solar panels produce clean energy without any harmful emissions or the need for continuous extraction. This significantly reduces the potential for environmental disasters and ensures the preservation of ecosystems.
In the ongoing debate between solar power and fossil fuels, the environmental sustainability aspect cannot be overlooked. The minimal land use and reduced habitat destruction associated with solar power make it a far more environmentally friendly option compared to fossil fuels. By embracing solar energy, we can move towards a greener future that prioritizes the preservation of our planet’s precious ecosystems.
Addressing concerns about solar power: manufacturing and disposal
One of the common concerns about solar power is related to the manufacturing process and the disposal of solar panels. Critics argue that the manufacturing of solar panels can have a negative impact on the environment, thus undermining the overall sustainability of solar power.
While it is true that the production of solar panels requires energy and resources, it is essential to consider the bigger picture. Solar panels have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels over their entire lifecycle. The emissions associated with manufacturing can be offset in just a few years of solar panel operation, leading to cleaner energy production for decades to come.
Moreover, the solar industry has been working diligently to improve manufacturing processes and reduce their environmental impact. Research and development efforts have led to advancements in eco-friendly manufacturing techniques, such as the use of recycled materials, reducing water consumption, and minimizing waste generation.
In terms of disposal, solar panels are designed to have a long lifespan, typically ranging from 25 to 30 years. At the end of their useful life, most solar panels can be recycled to recover valuable materials like silicon, glass, and metals. The recycling infrastructure for solar panels is continuously evolving, with more recycling facilities being established worldwide. This ensures that the materials are effectively reused, reducing the need for raw materials extraction and minimizing waste.
It is worth noting that the environmental impacts of manufacturing and disposal associated with fossil fuels are far more significant and long-lasting. Extraction activities, transportation, and combustion of fossil fuels release harmful greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change, air pollution, and environmental degradation.
In conclusion, while there are some concerns about the manufacturing and disposal of solar panels, the environmental benefits of solar power far outweigh these concerns. Continuous advancements in technology and increased focus on sustainable practices are making solar power an increasingly viable and environmentally friendly option for energy production.
The potential of solar power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels
The potential of solar power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels is a topic of great significance in today’s world. As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability continue to rise, the need for alternative sources of energy becomes increasingly apparent. Solar power, derived from the sun’s rays, offers a promising solution to combat our reliance on fossil fuels.
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite resources and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, solar power harnesses the abundant energy of the sun, a renewable and clean source. The sun’s energy is converted into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated solar power systems, allowing for a sustainable and environmentally friendly power generation process.
One of the key advantages of solar power is its potential to reduce carbon emissions. As solar panels generate electricity without burning fossil fuels, they help to mitigate the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. This not only improves air quality but also contributes to the global efforts of combating climate change.
Furthermore, solar power offers a decentralized energy production model. With solar panels installed on rooftops or in local communities, individuals and businesses can generate their own electricity, reducing the need for long-distance transmission and distribution of power. This localized approach not only increases energy efficiency but also enhances energy security and resilience, particularly in areas prone to power outages or disruptions.
Additionally, the installation and operation of solar power systems create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth. As the demand for solar panels and related technologies increases, so does the need for skilled professionals in the solar industry. This can lead to the creation of green jobs and promote sustainable economic development.
In conclusion, the potential of solar power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels cannot be underestimated. Its ability to generate clean and renewable energy, reduce carbon emissions, enhance energy security, and stimulate economic growth makes it a viable and attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, embracing solar power is a crucial step in achieving environmental sustainability and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Overcoming barriers to widespread adoption of Solar power
Overcoming the barriers to widespread adoption of solar power is crucial in the journey towards a sustainable future. While the benefits of solar power are well-known, there are still obstacles that hinder its broader implementation.
One significant challenge is the initial cost of installing solar panels. Although the long-term benefits outweigh the upfront investment, many individuals and businesses find it difficult to bear the initial expense. However, various incentives and financing options are available to make solar power more accessible. Government subsidies, tax credits, and grants can significantly reduce the cost, while leasing and power purchase agreements allow individuals and businesses to install solar panels without the upfront payment.
Another barrier is the intermittent nature of solar energy. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power generation depends on the availability of sunlight. This limitation can be overcome through the use of energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess energy during peak production times and use it during periods of low or no sunlight. Advancements in battery technology are making energy storage more efficient and affordable, further driving the adoption of solar power.
Furthermore, the complex regulations and policies surrounding solar power installation and grid connection pose challenges. Streamlining the permitting process, improving net metering policies, and ensuring fair compensation for excess energy fed back into the grid are essential steps towards encouraging widespread adoption of solar power.
Education and awareness also play a significant role in overcoming barriers. Providing accurate information about the benefits of solar power, dispelling myths, and showcasing successful case studies can help alleviate concerns and drive public acceptance.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, governments, and communities is crucial in addressing these barriers. By working together, we can overcome the challenges and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy future powered by solar energy.
Conclusion: Choosing a path towards a sustainable future

In conclusion, when it comes to choosing a path towards a sustainable future, the divide between solar power and fossil fuels becomes apparent. While fossil fuels have been the dominant energy source for centuries, their detrimental impact on the environment cannot be ignored. The extraction, transportation, and burning of these finite resources contribute to air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change.
On the other hand, solar power offers a viable and sustainable alternative. By harnessing the energy of the sun, solar power systems generate clean electricity without any harmful emissions or pollution. Solar panels have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a reliable and cost-effective option in the long run.
Transitioning from fossil fuels to solar power is not just an environmental choice; it is also an economic one. Solar power technology has become more advanced and affordable over the years, making it increasingly accessible to individuals, businesses, and governments. Investing in solar energy not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also creates job opportunities and stimulates economic growth.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of solar power extend beyond curbing climate change. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, we can also mitigate other environmental issues such as water pollution, land degradation, and habitat destruction associated with mining and drilling operations.
While there may be challenges in the transition to renewable energy, such as the need for infrastructure upgrades and policy support, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles. By embracing solar power and other renewable energy sources, we have the opportunity to create a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future for generations to come.
In the end, the choice is clear: to safeguard our planet and ensure a sustainable future, we must prioritize the adoption of solar power and move away from our reliance on fossil fuels. It is a decision that will not only benefit the environment but also pave the way for a greener and more prosperous world.
In conclusion, the debate between solar power and fossil fuels has become increasingly significant as we strive for a sustainable future. Through this blog post, we have delved into the environmental sustainability divide, shedding light on the advantages and disadvantages of both energy sources. While fossil fuels have long been the dominant source of energy, their harmful effects on the environment are undeniable.
Solar power, on the other hand, offers a clean and renewable alternative that not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also provides long-term economic benefits. The choice between these two options ultimately lies in our commitment to protecting the environment and investing in a greener future. By understanding the environmental sustainability divide, we can make informed decisions and collectively work towards a cleaner and healthier planet for generations to come.



